meta data for this page
This is an old revision of the document!
Group 5: Smart Meter - SIVIS
| Name | Student ID |
|---|---|
| Feruzjon Muyassarov | 0528844 |
| Krishna Teja Vaddepalli | 0528996 |
| Maliha Rahman Mishi | 0528815 |
Problem
- Energy from renewable sources not being utilized properly
- Best time for running appliances is not known
- Wastage of energy
- No clear monitoring available at individual appliance level
Concept
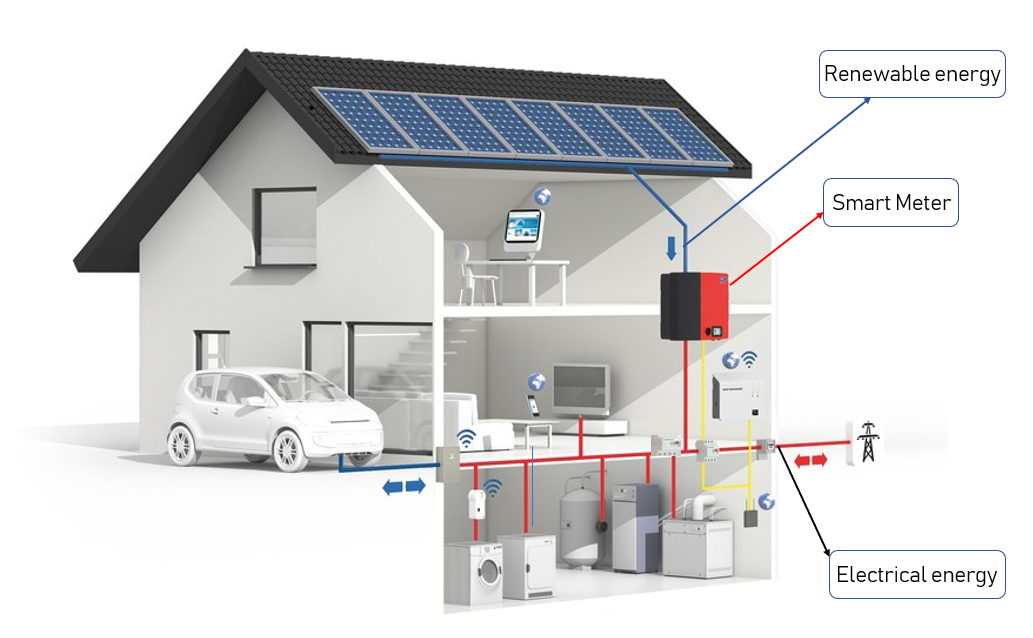
SIVIS is a smart meter which can solve the problems mentioned above. It can redirect all the extra energy to the power grid, suggests user to run the appliance when renewable energy is abundant, give statistics of energy usage at appliance level and also provide user with patterns of his/her energy usage. This also contacts different services like weather station, calendar of the owner and customizes some of its functions.
Motivation
- No such use of renewable energy
- User does not know what is the energy being used by individual appliance
- User has no way to determine when can he run appliances so that they run on renewable energy
- User doesn’t get reports on the renewable energy usage
Features
- Uses Renewable Energy and power grid
- Supplies extra energy to power grid
- Energy saving
- Energy supply
- Reduces CO2 emission
- Flexibility of control
- Suggestion on equipment usage
Architecture
Scenario
- Stark wakes up from bed with the curtains and windows being opened, at the time he set his alarm, by his SIVIS.
- He plans to wash his clothes and so leaves his clothes in the washing machine and asks SIVIS to wash the clothes for him. It immediately checks the local weather station updates and learns that there are no clouds and the Sun is going to be up all day with maximum intensity from 11:00 hrs to 13:00 hrs. Getting the timings, it would schedule washing machine to run during the time where maximum energy is generated
- Stark has a smart water controller set up in his house and hence uses less amount of water to take a shower than he used before setting it up
- He prepares to leave for office in his electric car. He goes to his garage to take out the car. The car gets charged wirelessly when it is parked in the garage and hence he doesn’t need to worry about charging the car
- In hurry of leaving to office, he forgets to turn off the lights and other equipment in the living room. SIVIS recognises that there is no one present in the living room and turns off all the appliances
- After he leaves to office, SIVIS gets a message from Stark stating that his friends are visiting him that evening at 17:00 hrs and hence cool the living room to 23°. SIVIS, with the information collected from the weather station gets to know that the weather is going to cool down from 15:00 hrs and hence opens the windows to cool the house from 16:00 hrs instead of using the air conditioning
- When he comes back home in the evening, SIVIS provides Stark with the amount of energy used that day and the percentage of renewable energy used and what amount of renewable energy is sent to the power grid. He also gets to see energy consumed by individual appliances in each room of the house.
Sustainability
- Renewable energy would be fully consumed i.e, no wastage of renewable energy
- System checks weather updates and runs the appliances when the renewable energy is available to run the appliance
- No storage of energy in batteries giving no scope for pollution when batteries are to be disposed
- Extra energy being supplied to power grids would reduce the necessity of energy from non-renewable sources of energy
- Reports of energy consumption is provided to user which can bring a change in user behavior
KNX-Communication protocol
- KNX - is a system of sensors and actuators joined together by a “bus cable”.
- Administered by the KNX Association;
- 339 members/manufacturers from 37 countries;
- KNX devices are installed, programmed and parameterised by fully qualified system integrators;
- Accommodate wide range of functions;
- KNX based products are compatible with products from all manufactures;
- Supports all communication including Powerline (PL), Radio Frequency (RF), IP/Ethernet/WLAN
- System (power supplies, programming interfaces) and end devices (sensors and actuators);
Disadvantages
- Smart Meter: SIVIS can be expensive (now).
- Time consuming in terms of generation and load of renewable energy.
- Maintaining grid reliability requires precise synchronization of voltage and current.